
Kibana is a platform that visualizes data on the Elastic Stack. This page shows how to use the CockroachDB module for Metricbeat to collect metrics exposed by your CockroachDB Self-Hosted cluster's Prometheus endpoint in Elasticsearch and how to visualize those metrics with Kibana.
To export metrics from a CockroachDB Cloud cluster, refer to Export Metrics From a CockroachDB Dedicated Cluster instead of this page.
In this tutorial, you will enable the CockroachDB module for Metricbeat and visualize the data in Kibana.
For more information about using the CockroachDB module for Metricbeat, see the Elastic documentation.
If you run into problems with this integration, please file an issue on the Beats issue tracker.
Before you begin
Either of the following:
- Hosted Elasticsearch Service with Metricbeat configured
- Self-managed Elastic Stack with Metricbeat installed
This tutorial assumes that you have started a secure CockroachDB cluster. CockroachDB Cloud does not expose a compatible monitoring endpoint.
Step 1. Enable CockroachDB module
From your Metricbeat installation directory, run:
./metricbeat modules enable cockroachdb
Configure security certificates
Open modules.d/cockroachdb.yml in your Metricbeat installation directory.
Follow the steps in the Elastic documentation to enable SSL on the CockroachDB module.
For example, if you used cockroach cert to secure your cluster, the YAML should look like:
- module: cockroachdb
metricsets: ['status']
period: 10s
hosts: ['localhost:8080']
enabled: true
ssl.verification_mode: full
ssl.certificate_authorities: "/custom/dir/path/ca.crt"
ssl.certificate: "/custom/dir/path/client.root.crt"
ssl.key: "/custom/dir/path/client.root.key"
ssl.certificate_authorities, ssl.certificate, and ssl.key should specify the full file paths to your CA certificate, client certificate, and client key, respectively.
Step 2. Start Metricbeat
Load the Kibana dashboards (this may take a few moments):
./metricbeat setup
Launch Metricbeat:
./metricbeat -e
Step 3. View CockroachDB dashboards on Kibana
Open the Kibana web interface and click Dashboard.
Search for the CockroachDB dashboard:
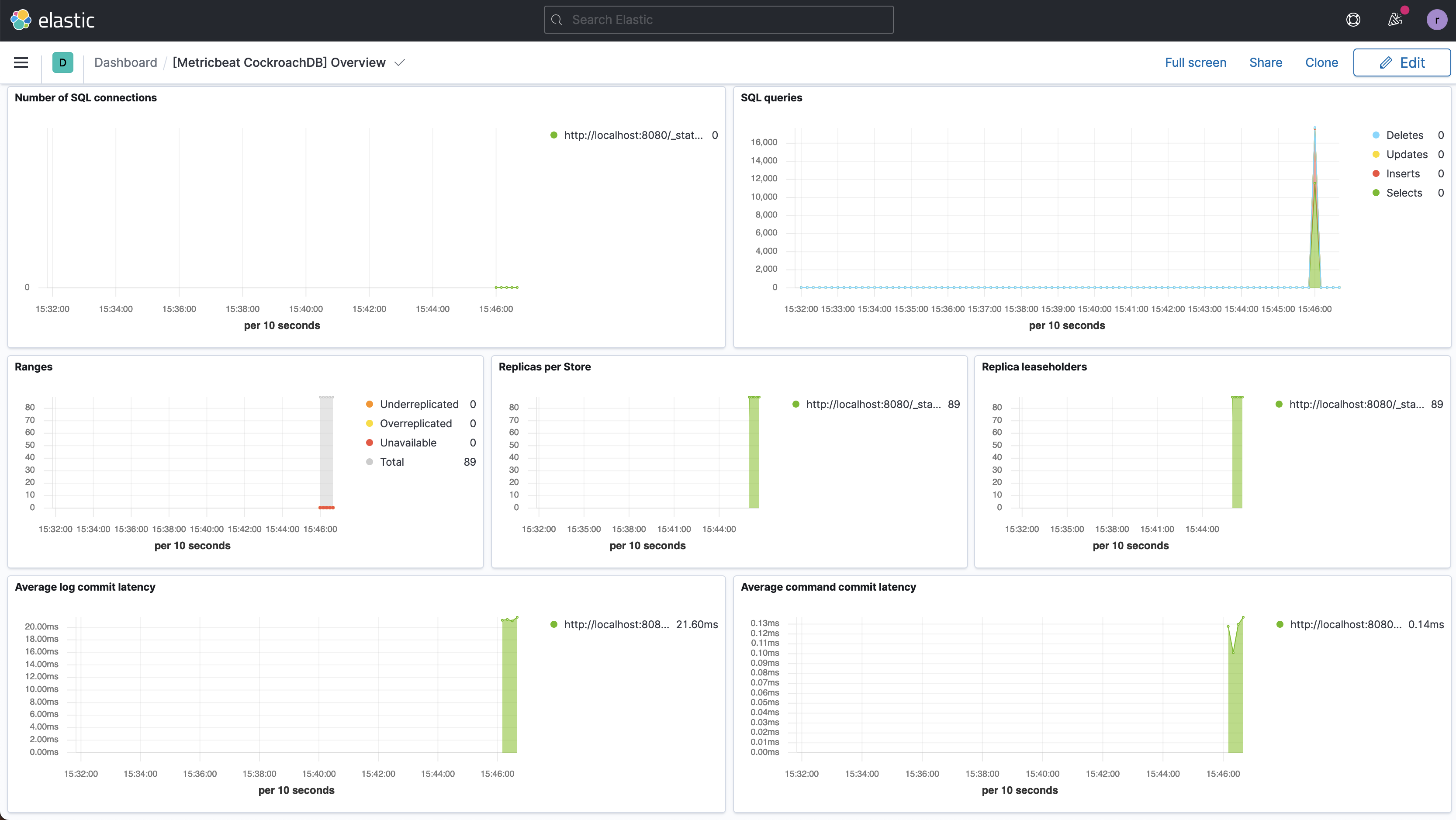
Click the dashboard title to open the dashboard, which presents metrics on replicas and query performance:
Step 4. Run a sample workload
To test the dashboard functionality, use cockroach workload to run a sample workload on the cluster.
Initialize the workload for MovR, a fictional vehicle-sharing company:
cockroach workload init movr 'postgresql://root@localhost:26257?sslcert=certs%2Fclient.root.crt&sslkey=certs%2Fclient.root.key&sslmode=verify-full&sslrootcert=certs%2Fca.crt'
Run the MovR workload for 5 minutes:
cockroach workload run movr --duration=5m 'postgresql://root@localhost:26257?sslcert=certs%2Fclient.root.crt&sslkey=certs%2Fclient.root.key&sslmode=verify-full&sslrootcert=certs%2Fca.crt'
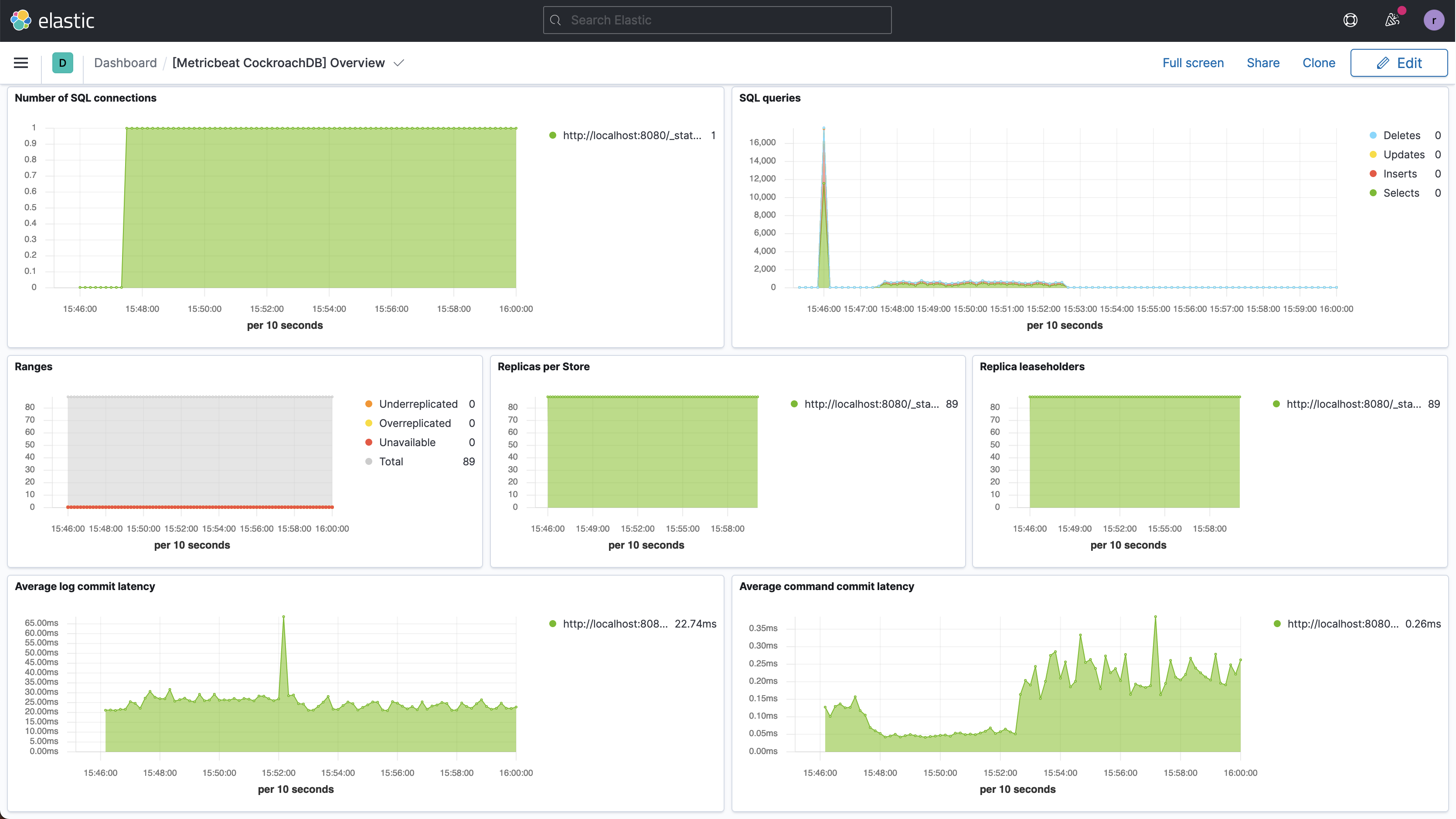
Click Refresh. The query metrics will appear on the dashboard:
Step 5. Disable DB Console's local storage of metrics (optional)
If you rely on external tools such as Kibana for storing and visualizing your cluster's time-series metrics, Cockroach Labs recommends that you disable the DB Console's storage of time-series metrics.
When storage of time-series metrics is disabled, the cluster continues to expose its metrics via the Prometheus endpoint. The DB Console stops storing new time-series cluster metrics and eventually deletes historical data. The Metrics dashboards in the DB Console are still available, but their visualizations are blank. This is because the dashboards rely on data that is no longer available. You can create queries, visualizations, and alerts in Kibana based on the data it is collecting from your cluster's Prometheus endpoint.